Installing with conda#
Conda packages can be installed by running the following command:
conda install <package>
When conda installs a package, it is automatically added to your active
environment. These packages are collections of files and directories
that make up everything you need to use that particular
library or software. For Python packages, these are primarily Python
files that can be imported into other Python applications, but for compiled
software packages, such as ffmpeg, these are typically binary executables
you use directly on your computer.
Note
If you would like to learn more about how environments are structured, head over to conda environments.
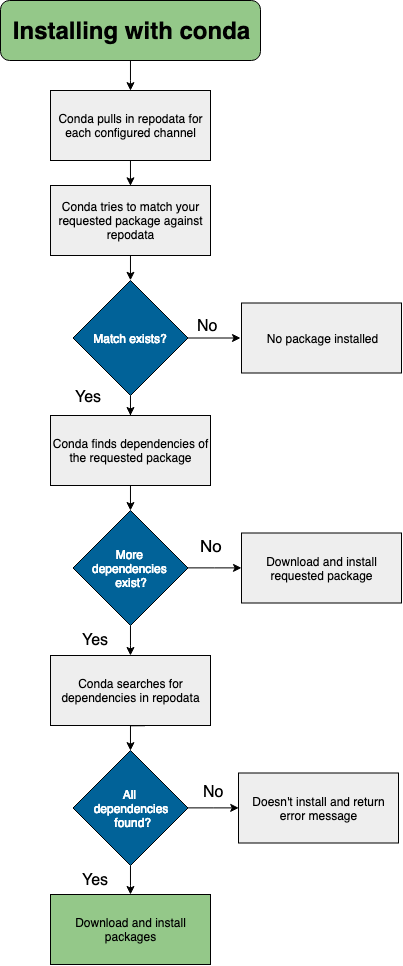
Below is a more precise overview of everything that happens during the installation process for a single package:
Currently configured channels (e.g.
defaultsorconda-forge) are read in order of priorityRepodata for these configured channels is downloaded and read
The repodata is searched for the package, starting with the highest priority channel first
Once the package is found, conda makes a separate download request and then installs it
This process then repeats for each of the package's dependencies, if there are any
A graphic illustration of this process is shown below:
Conda update versus conda install#
conda update updates packages to the latest compatible version.
conda install can be used to install any version.
Example:
If Python 2.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python 2 is 2.7.5, then
conda update pythoninstalls Python 2.7.5. It does not install Python 3.If Python 3.7.0 is currently installed, and the latest version of Python is 3.9.0, then
conda install python=3installs Python 3.9.0.
Conda uses the same rules for other packages. conda update always installs the highest version with the same major version number, whereas conda install always installs the highest version.
Installing conda packages offline#
To install conda packages offline, run:
conda install /path-to-package/package-filename.tar.bz2/
If you prefer, you can create a /tar/ archive file containing
many conda packages and install them all with one command:
conda install /packages-path/packages-filename.tar
Note
If an installed package does not work, it may be missing dependencies that need to be resolved manually.
Installing packages directly from the file does not resolve dependencies.
Installing conda packages with a specific build number#
If you want to install conda packages with the correct package specification, try
pkg_name=version=build_string. Read more about build strings and package naming conventions.
Learn more about package specifications and metadata.
For example, if you want to install llvmlite 0.31.0dev0 on Python 3.7.8, you would enter:
conda install -c numba/label/dev llvmlite=0.31.0dev0=py37_8